
Green Tea Catechins, (−)‐Catechin Gallate, and (−)‐Gallocatechin Gallate are Potent Inhibitors of ABA‐Induced Stomatal Closure
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Advanced Science"
DOI: 10.1002/advs.202201403
Abstract: Stomatal movement is indispensable for plant growth and survival in response to environmental stimuli. Cytosolic Ca2+ elevation plays a crucial role in ABA‐induced stomatal closure during drought stress; however, to what extent the Ca2+ movement… read more here.
Keywords: catechin gallate; induced stomatal; stomatal closure; aba induced ... See more keywords
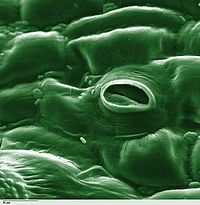
Mechanism of Stomatal Closure in Plants Exposed to Drought and Cold Stress.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Advances in experimental medicine and biology"
DOI: 10.1007/978-981-13-1244-1_12
Abstract: Drought is one of the abiotic stresses which impairs the plant growth/development and restricts the yield of many crops throughout the world. Stomatal closure is a common adaptation response of plants to the onset of… read more here.
Keywords: drought; closure; stomatal closure; signaling components ... See more keywords

The E3 ligase MREL57 modulates microtubule stability and stomatal closure in response to ABA
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Nature Communications"
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22455-y
Abstract: Regulation of stomatal movement is critical for plant adaptation to environmental stresses. The microtubule cytoskeleton undergoes disassembly, which is critical for stomatal closure in response to abscisic acid (ABA). However, the mechanism underlying this regulation… read more here.
Keywords: closure; stomatal closure; mrel57; closure response ... See more keywords

PeABF3 Enhances Drought Tolerance via Promoting ABA-induced Stomatal Closure by directly Regulating PeADF5 in Poplar.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Journal of experimental botany"
DOI: 10.1093/jxb/eraa383
Abstract: Water availability is a main limiting factor for plant growth, development and distribution throughout the world. Stomatal movement mediated by abscisic acid (ABA) is particularly important for drought adaptation, but the molecular mechanisms in trees… read more here.
Keywords: stomatal closure; aba; drought tolerance; peabf3 ... See more keywords

Stomatal response to isothiocyanates in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Journal of experimental botany"
DOI: 10.1093/jxb/eraa420
Abstract: Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) induces stomatal closure accompanied by reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and glutathione (GSH) depletion in Arabidopsis thaliana. In this study, stomatal responses to three other isothiocyanates (ITCs), benzyl isothiocyanate (BITC), sulforaphane (SFN),… read more here.
Keywords: stomatal closure; ros production; decrease stomatal; arabidopsis thaliana ... See more keywords

The JASMONATE ZIM-domain-OPEN STOMATA1 cascade integrates jasmonic acid and abscisic acid signaling to regulate drought tolerance by mediating stomatal closure in poplar.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Journal of experimental botany"
DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erac418
Abstract: Drought, which directly affected the yield of crops and trees, is a natural disaster with a profound impact on the economy. Improved water-use efficiency (WUE) and drought tolerance are currently known to be the relatively… read more here.
Keywords: drought tolerance; acid; stomatal closure; drought ... See more keywords

Glucose triggers stomatal closure mediated by basal signaling through HXK1 and PYR/RCAR receptors in Arabidopsis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Journal of Experimental Botany"
DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ery024
Abstract: Glucose-triggered stomatal closure is dependent on basal ABA signaling through PYR/RCAR receptors, CDPK6, and glucose signaling mediated by hexokinase1 (HXK1) in Arabidopsis. read more here.
Keywords: pyr rcar; rcar receptors; stomatal closure;

Mitochondrial H2S donor AP39 induces stomatal closure by modulating guard cell mitochondrial activity.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Plant physiology"
DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiac591
Abstract: Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) is a gaseous signaling molecule involved in numerous physiological processes in plants, including gas exchange with the environment through the regulation of stomatal pore width. Guard cells are pairs of specialized epidermal… read more here.
Keywords: stomatal closure; guard; activity; mitochondrial activity ... See more keywords

Abscisic acid increases hydrogen peroxide in mitochondria to facilitate stomatal closure
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Plant Physiology"
DOI: 10.1101/2022.01.11.475946
Abstract: Abscisic acid (ABA) drives stomatal closure to minimize water loss due to transpiration in response to drought. We examined the subcellular location of ABA increased accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in guard cells that… read more here.
Keywords: stomatal closure; aba; closure; guard cell ... See more keywords

Hydrogen Sulfide Increases Production of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent Hydrogen Peroxide and Phospholipase D-Derived Phosphatidic Acid in Guard Cell Signaling1
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Plant Physiology"
DOI: 10.1104/pp.17.01636
Abstract: Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an important gaseous signaling molecule in plants that participates in stress responses and development. l-Cys desulfhydrase 1, one of the enzymatic sources of H2S in plants, participates in abscisic acid-induced stomatal… read more here.
Keywords: production; hydrogen; pld; stomatal closure ... See more keywords

The Tomato DELLA Protein PROCERA Promotes Abscisic Acid Responses in Guard Cells by Upregulating an Abscisic Acid Transporter.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Plant physiology"
DOI: 10.1104/pp.20.00485
Abstract: Plants reduce transpiration through stomatal closure to avoid drought stress. While abscisic acid (ABA) has a central role in the regulation of stomatal closure under water-deficit conditions, we demonstrated in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) that a… read more here.
Keywords: abscisic acid; ait1; stomatal closure; guard cells ... See more keywords