Metabolomics Analysis of Bacterial Pathogen Burkholderia thailandensis and Mammalian Host Cells in Co-culture.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "ACS infectious diseases"
DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00233
Abstract: The Tier 1 HHS/USDA Select Agent Burkholderia pseudomallei is a bacterial pathogen that is highly virulent when introduced into the respiratory tract and intrinsically resistant to many antibiotics. Transcriptomic- and proteomic-based methodologies have been used… read more here.
Keywords: culture; infection; burkholderia; thailandensis ... See more keywords

A coevolution experiment between Flavobacterium johnsoniae and Burkholderia thailandensis reveals parallel mutations that reduce antibiotic susceptibility.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Microbiology"
DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001267
Abstract: One interference mechanism of bacterial competition is the production of antibiotics. Bacteria exposed to antibiotics can resist antibiotic inhibition through intrinsic or acquired mechanisms. Here, we performed a coevolution experiment to understand the long-term consequences… read more here.
Keywords: coevolution experiment; johnsoniae; thailandensis; susceptibility ... See more keywords

Burkholderia thailandensis Methylated Hydroxyalkylquinolines: Biosynthesis and Antimicrobial Activity in Cocultures
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Applied and Environmental Microbiology"
DOI: 10.1128/aem.01452-20
Abstract: The soil bacterium Burkholderia thailandensis produces 2-alkyl-4(1H)-quinolones that are mostly methylated 4-hydroxyalkenylquinolines, a family of relatively unstudied metabolites similar to molecules also synthesized by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Several of the methylated 4-hydroxyalkenylquinolines have antimicrobial activity against… read more here.
Keywords: alkyl quinolones; thailandensis; biology; methylated hydroxyalkenylquinolines ... See more keywords
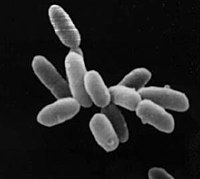
Changes in polyhydroxyalkanoate granule accumulation makes optical density measurement an unreliable method for estimating bacterial growth in Burkholderia thailandensis.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Canadian journal of microbiology"
DOI: 10.1139/cjm-2019-0342
Abstract: Optical density (OD) measurement is the standard method used in microbiology for estimating bacterial concentrations in cultures. However, most studies do not compare these measurements with viable cell counts and assume that they reflect the… read more here.
Keywords: growth; thailandensis; pha; density ... See more keywords

Presence of B. thailandensis and B. thailandensis expressing B. pseudomallei-like capsular polysaccharide in Thailand, and their associations with serological response to B. pseudomallei
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases"
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006193
Abstract: Background Burkholderia pseudomallei is an environmental Gram-negative bacillus and the cause of melioidosis. B. thailandensis, some strains of which express a B. pseudomallei-like capsular polysaccharide (BTCV), is also commonly found in the environment in Southeast… read more here.
Keywords: btcv; presence; thailandensis; thailand ... See more keywords

Detection and differentiation of Burkholderia species with pathogenic potential in environmental soil samples
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "PLoS ONE"
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245175
Abstract: The Burkholderia pseudomallei phylogenetic cluster includes B. pseudomallei, B. mallei, B. thailandensis, B. oklahomensis, B. humptydooensis and B. singularis. Regarded as the only pathogenic members of this group, B. pseudomallei and B. mallei cause the… read more here.
Keywords: pathogenic potential; soil samples; detection; thailandensis ... See more keywords

PKC-η-MARCKS Signaling Promotes Intracellular Survival of Unopsonized Burkholderia thailandensis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology"
DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00231
Abstract: Pathogenic Burkholderia rely on host factors for efficient intracellular replication and are highly refractory to antibiotic treatment. To identify host genes that are required by Burkholderia spp. during infection, we performed a RNA interference (RNAi)… read more here.
Keywords: burkholderia; intracellular survival; thailandensis; infection ... See more keywords