
Mice Lacking Wnt9a or Wnt4 Are Prone to Develop Spontaneous Osteoarthritis With Age and Display Alteration in Either the Trabecular or Cortical Bone Compartment
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Journal of Bone and Mineral Research"
DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.4569
Abstract: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative disease of the joint, with a complex multifactorial not yet fully understood etiology. Over the past years, the Wnt signaling pathway has been implicated in osteoarthritis. In a recent… read more here.
Keywords: bone; age; osteoarthritis; wnt4 ... See more keywords

Expression and function of WNT4 involved in larvae development and limb regeneration in Portunus trituberculatus
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Journal of Oceanology and Limnology"
DOI: 10.1007/s00343-020-9291-6
Abstract: The wingless-related integration site (WNT) proteins are a family of secreted glycoproteins that are evolutionarily conserved and are believed to be involved in evolution in vertebrates and invertebrates. WNT signaling pathways may be associated with… read more here.
Keywords: trituberculatus; wnt4; expression; limb regeneration ... See more keywords

Carotid artery ligation induced intimal thickening and proliferation is unaffected by ageing
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling"
DOI: 10.1007/s12079-017-0431-5
Abstract: Following interventions to treat atherosclerosis, such as coronary artery bypass graft surgery, restenosis occurs in approximately 40% of patients. Identification of proteins regulating intimal thickening could represent targets to prevent restenosis. Our group previously demonstrated… read more here.
Keywords: artery; intimal thickening; wnt4; carotid artery ... See more keywords

Wnt4 is significantly upregulated during the early phases of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28595-4
Abstract: Wnt4 is a secreted growth factor associated with renal tubulogenesis. Our previous studies identified that renal and urinary Wnt4 are upregulated following ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice, but the roles of Wnt4 in other forms of… read more here.
Keywords: wnt4; urinary wnt4; acute kidney; cisplatin induced ... See more keywords

O017 Dupuytren's disease (DD): WNT4 knockdown in normal skin fibroblasts leads to ‘DD-like’ changes in the transcriptome
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "British Journal of Surgery"
DOI: 10.1093/bjs/znad101.017
Abstract: Dupuytren's disease (DD), a fibro-proliferative disorder of unknown aetiology, affects the palm and is characterised by progressive fibrosis, thickening of palmar fascia, and excess collagen deposition. Patients present with nodules, causing flexion deformity in ∼50%,… read more here.
Keywords: like changes; skin; changes transcriptome; skin fibroblasts ... See more keywords
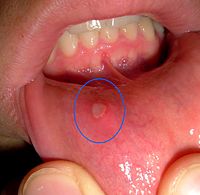
Wnt4 regulates bone metabolism through IKK-NF-κB and ROCK signaling under occlusal traumatic periodontitis.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Journal of periodontal research"
DOI: 10.1111/jre.12975
Abstract: BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVE Occlusal trauma is one of the most important local contributing factors of periodontitis. It has been reported that Wnt4, a noncanonical Wnt ligand, can inhibit osteoclast formation and inflammation and promote bone… read more here.
Keywords: occlusal trauma; rock signaling; periodontitis; trauma periodontitis ... See more keywords

Estrogen Regulation of mTOR Signaling and Mitochondrial Function in Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Cell Lines Requires WNT4
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Cancers"
DOI: 10.3390/cancers12102931
Abstract: Simple Summary Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is a common but understudied breast cancer subtype. ILC is presumed to be a low-risk disease in part because nearly all ILCs contain the estrogen receptor (ER). However, we… read more here.
Keywords: wnt4; mtor signaling; estrogen; invasive lobular ... See more keywords