
One‐step purification and regulation of fructose 1,6‐bisphosphatase from the liver of the freeze‐tolerant wood frog, Rana sylvatica
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Cell Biochemistry and Function"
DOI: 10.1002/cbf.3710
Abstract: The wood frog (Rana sylvatica) undergoes numerous changes to its physiology and metabolic processes to survive the winter months, including adaptations that let them endure whole‐body freezing. The regulation of key enzymes of central carbohydrate… read more here.
Keywords: liver; frog rana; wood frog; regulation ... See more keywords

Metal Changes in Pre- and Post-metamorphic Wood Frog (Lithobates sylvaticus) Tadpoles: Implications for Ecotoxicological Studies
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology"
DOI: 10.1007/s00244-020-00735-w
Abstract: The development of anuran larvae from hatchling through metamorphosis is a particularly sensitive life stage that often is studied to assess adverse effects of water pollution, such as metal contamination. As an integral part of… read more here.
Keywords: metal; wood frog; metamorphic climax; wood ... See more keywords

Purification of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) from wood frog (Rana sylvatica) liver and its regulation in response to ice-nucleation and subsequent whole-body freezing
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry"
DOI: 10.1007/s11010-018-3468-8
Abstract: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS1) represents an important regulatory enzyme of the urea cycle that mediates the ATP-driven reaction ligating ammonium, carbonate, and phosphate to form carbamoyl phosphate. The freeze-tolerant wood frog (Rana sylvatica or… read more here.
Keywords: wood frog; cps1; phosphate; carbamoyl phosphate ... See more keywords

Exposure to the antifouling chemical medetomidine slows development, reduces body mass, and delays metamorphosis in wood frog (Lithobates sylvaticus) tadpoles
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Environmental Science and Pollution Research"
DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-1204-2
Abstract: Antifouling chemicals have a long history of causing toxicity to aquatic organisms. We measured growth and developmental timing in wood frog tadpoles exposed to the antifouling chemical medetomidine (10 nM–10 μM) starting at two different developmental stages… read more here.
Keywords: medetomidine; chemical medetomidine; wood frog; metamorphosis ... See more keywords
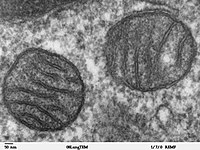
Regulation of pyruvate kinase in skeletal muscle of the freeze tolerant wood frog, Rana sylvatica.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Cryobiology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2017.06.002
Abstract: The wood frog (Rana sylvatica) can survive the winter in a frozen state, in which the frog's tissues are also exposed to dehydration, ischemia, and anoxia. Critical to wood frog survival under these conditions is… read more here.
Keywords: pyruvate; muscle; frog; frog rana ... See more keywords

TonEBP/NFAT5 regulates downstream osmoregulatory proteins during freeze-thaw stress in the wood frog.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Cryobiology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2017.09.003
Abstract: Rana sylvatica, known as the wood frog, can survive extremely cold temperatures during winter by undergoing full-body freezing, where it tolerates freezing of 65-70% of its total body water. During freezing, cellular dehydration decreases damage… read more here.
Keywords: aldose reductase; osmoregulatory; freeze thaw; osmoregulatory proteins ... See more keywords

Future winters present a complex energetic landscape of decreased costs and reduced risk for a freeze-tolerant amphibian, the Wood Frog (Lithobates sylvaticus).
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Global change biology"
DOI: 10.1111/gcb.15321
Abstract: Winter climate warming is rapidly leading to changes in snow depth and soil temperatures across mid- and high-latitude ecosystems, with important implications for survival and distribution of species that overwinter beneath the snow. Amphibians are… read more here.
Keywords: winter; tolerant amphibian; climate; freeze tolerant ... See more keywords