Photo from wikipedia
Histamine plays pleiotropic roles as a neurotransmitter in the physiology of brain function, this includes the maintenance of wakefulness, appetite regulation and memory retrieval. Since numerous studies have revealed an… Click to show full abstract
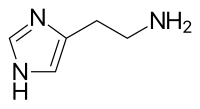
Histamine plays pleiotropic roles as a neurotransmitter in the physiology of brain function, this includes the maintenance of wakefulness, appetite regulation and memory retrieval. Since numerous studies have revealed an association between histaminergic dysfunction and diverse neuropsychiatric disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia, a large number of compounds acting on the brain histamine system have been developed to treat neurological disorders. In 2016, pitolisant, which was developed as a histamine H3 receptor inverse agonist by Schwartz and colleagues, was launched for the treatment of narcolepsy, emphasising the prominent role of brain histamine on wakefulness. Recent advances in neuroscientific techniques such as chemogenetic and optogenetic approaches have led to remarkable progress in the understanding of histaminergic neural circuits essential for the control of wakefulness. In this review article, we summarise the basic knowledge about the histaminergic nervous system and the mechanisms underlying sleep/wake regulation that are controlled by the brain histamine system.
Journal Title: British Journal of Pharmacology
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!