
Hypoxia and hyperoxia differentially control proliferation of rat neural crest stem cells via distinct regulatory pathways of the HIF1α–CXCR4 and TP53–TPM1 proteins
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Developmental Dynamics"
DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.24481
Abstract: Background: Neural crest stem cells (NCSCs) are a population of adult multipotent stem cells. We are interested in studying whether oxygen tensions affect the capability of NCSCs to self‐renew and repair damaged tissues. NCSCs extracted… read more here.
Keywords: proliferation; tpm1; stem cells; rat ... See more keywords

Left ventricular non-compaction with Ebstein anomaly attributed to a TPM1 mutation.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "European journal of medical genetics"
DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2017.10.003
Abstract: Left ventricular non-compaction (cardiomyopathy) (LVN(C)) is a rare hereditary cardiac condition, resulting from abnormal embryonic myocardial development. While it mostly occurs as an isolated condition, association with other cardiovascular manifestations such as Ebstein anomaly (EA)… read more here.
Keywords: ventricular non; ebstein anomaly; tpm1; non compaction ... See more keywords
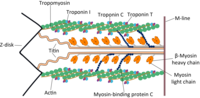
Further Investigation into the Biochemical Effects of Phosphorylation of Tropomyosin Tpm1.1(α). Serine-283 Is in Communication with the Midregion.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Biochemistry"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00882
Abstract: The phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of tropomyosin Tpm1.1(α) are prepared from adult rabbit heart and compared biochemically. Electrophoresis confirms the high level of enrichment of the chromatography fractions and is consistent with a single site… read more here.
Keywords: investigation biochemical; tropomyosin tpm1; biochemical effects; tpm1 ... See more keywords

Accumulation of systematic TPM1 mediates inflammation and neuronal remodeling by phosphorylating PKA and regulating the FABP5/NF‐κB signaling pathway in the retina of aged mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Aging Cell"
DOI: 10.1111/acel.13566
Abstract: The molecular mechanisms underlying functional decline during normal brain aging are poorly understood. Here, we identified the actin‐associated protein tropomyosin 1 (TPM1) as a new systemic pro‐aging factor associated with function deficits in normal aging… read more here.
Keywords: systematic tpm1; tpm1; retina aged; aged mice ... See more keywords

Considering the downregulation of Tpm1.6 and Tpm1.7 in squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus as a potent biomarker.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Personalized medicine"
DOI: 10.2217/pme-2018-0015
Abstract: AIM Squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus (SCCE) is an aggressive disease with a poor prognosis. Tropomyosins attach to actin microfilaments, providing its stability. Nonmuscle cells express Tpm isoforms such as Tpm1.6 and Tpm1.7 which are… read more here.
Keywords: cell carcinoma; squamous cell; tpm1 tpm1; carcinoma esophagus ... See more keywords

MicroRNA-107 Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting Tropomyosin 1.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Oncology research"
DOI: 10.3727/096504017x14882829077237
Abstract: Osteosarcoma is the most common primary bone malignancy manifested predominantly in children and young adults. Studies indicate that miR-107 is involved in the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma and that tropomyosin 1 (TPM1) acts as a tumor… read more here.
Keywords: mir 107; migration invasion; osteosarcoma; tpm1 ... See more keywords